Solar PV Plant: Engineering, Types, Working Principle, and Cost Analysis
A solar PV plant is now far more than a renewable energy source; it is a mission-critical grid asset that can live reliably for 25 or more years. Large-scale solar photovoltaic power plants and C&I solar photovoltaic power plants must integrate seamlessly into transmission networks and comply with strict electrical, safety, and regulatory requirements.
Modern PV plants are designed to work well, are strong, and are financially viable, with detailed engineering and power system analyses as well as grid codes and international standards. With the growth in utility-scale installations and their complexities, engineering excellence and system integration have become a crucial part of the project.
What Is a Solar PV Plant?
A solar PV plant is a power generation system that operates from sunlight, producing electricity through the photovoltaic effect. It produces no mechanical resistance and is therefore highly reliable and scalable when solar radiation strikes photovoltaic cells.
In contrast to the small rooftop systems, the photovoltaic power plant is created as a complete infrastructure project. This includes power generation systems, electric balance of systems, security systems, networks and grid interfacing systems. Engineering design ensures the safe operation of the photovoltaic plant in different grid configurations while meeting national regulations, utility requirements, and long-run performance expectations.
What Is a Solar Power Plant? How It Works and Types
Working of a Solar Photovoltaic Power Plant

Solar photovoltaic power plants are operated in a grid-compliant electrical and control system.
Solar radiation is absorbed by PV modules and generates DC electricity at the cell level. The DC power is aggregated at the string and array levels through DC cables and combiner boxes for efficient power distribution. Inverter systems convert DC into grid-synchronised AC power while maintaining voltage, frequency, and power quality requirements.
Transformers increase the output AC to medium or high voltages to minimise transmission losses. Power is then sent from a switchyard and transmission line to the grid. Protection relays, meters and SCADA platforms monitor system performance, identify faults, and ensure safe solar photovoltaic power plant operation in all conditions.
Top Solar Consultants in India
Types of Solar PV Plants
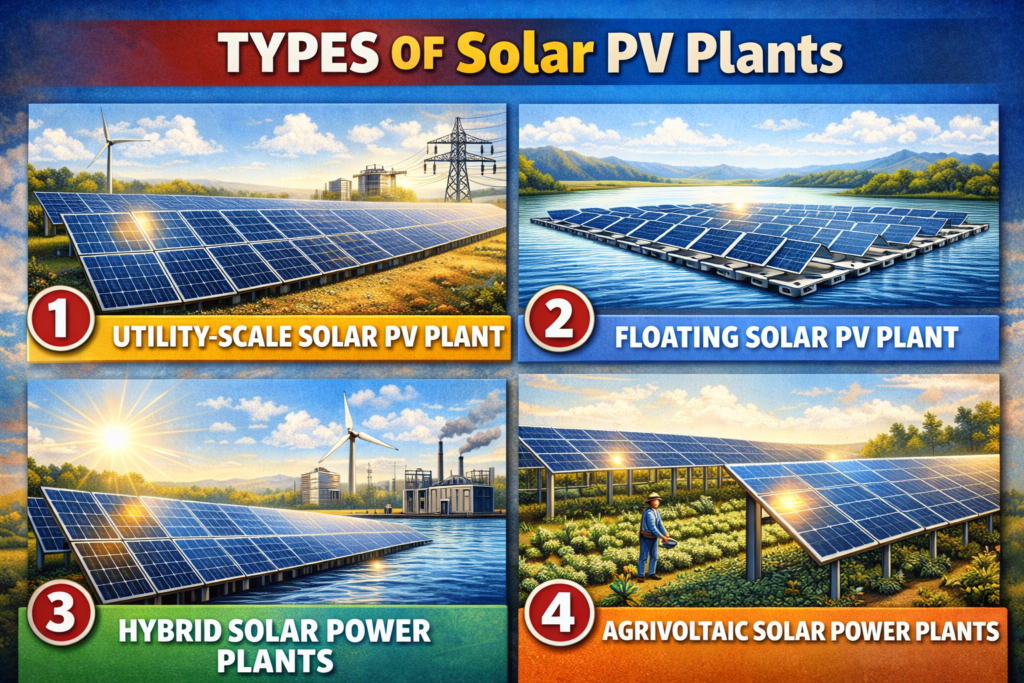
Solar PV plants are also grouped into deployment environment, grid function and land use strategy. More and more plant types are being developed in order to address land scarcity, grid stability, hybrid energy integration, and sustainable development goals.
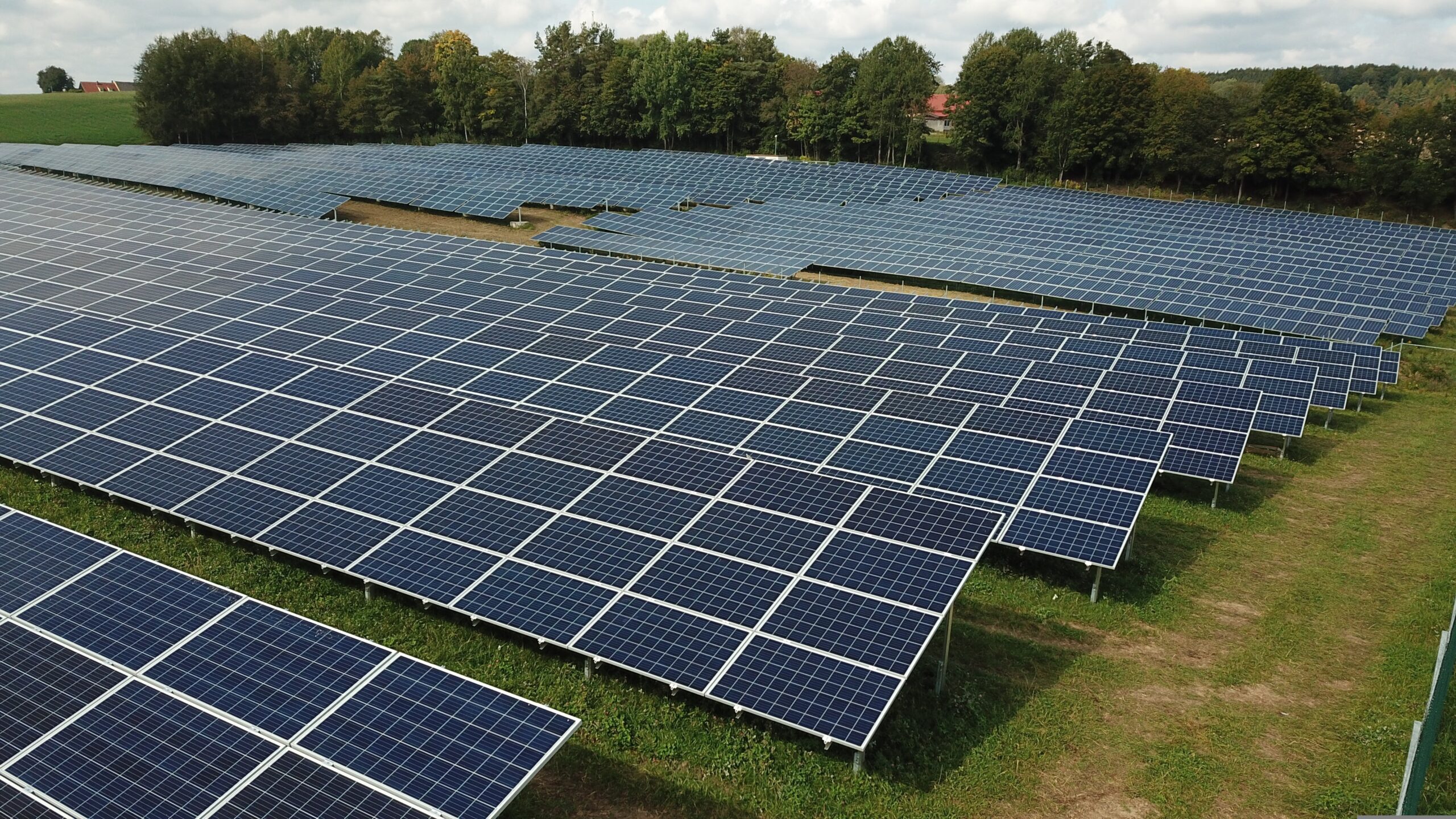
Utility-Scale Solar PV Plant
Amounts of solar photovoltaic power plants for utility applications generally range from 10 MW to several gigawatts. These plants are connected directly to transmission networks and supply bulk power to utilities or power markets.
Specifically, engineering focus areas are power evacuation design, reactive power management, fault level assessment, and grid code compliance. Power system studies are an important factor in ensuring continuity of operation, and land optimisation and environmental clearances can play a large role in project success and completion.
Floating Solar PV Plant
A floating solar PV plant is installed on reservoirs and lakes, thus reducing land use. Water can naturally cool the modules, which can subsequently improve the solar PV power generation.
Nevertheless, floating solar photovoltaic plant construction presents problems with structural stability, anchoring systems, wave impact, humidity, and corrosion resistance. Electrical safety and maintenance planning are more complex compared to ground-mounted photovoltaic power stations.
Hybrid Solar Power Plants
A hybrid solar power plant uses solar and other sources of electricity for greater reliability and energy availability. A hybrid solar-wind power plant and a hybrid solar hydro power plant can support an equilibrium between variability and maximise grid utilisation.
A hybrid solar power plant requires high-tech controls, forecasting machinery and coordinated protections. While engineering complexity increases, hybridisation also increases dispatchability and system efficiency.
Agrivoltaic Solar Power Plants
Agrivoltaic solar power plants combine the use of agriculture and solar energy by lifting PV panels off of farms. This increases land productivity and reduces evaporation and heat stress for some crops.
The construction industry has to address higher structural height, wind loading, and shading optimisation. Agrivoltaic photovoltaic plants are emerging in those areas where land availability and sustainability are key considerations.
Best Solar Power Plant Consultants in India
Solar PV Power Generation Process
The production of photovoltaic power is accompanied by a detailed solar resource assessment, including irradiation and climatic data. These inputs dictate expected energy yield and plant size.
Capacity Utilisation Factor (CUF) and Performance Ratio (PR) are two main performance indicators, indicating the efficiency of a PV power plant in converting sunlight to electricity. Losses from soiling, temperature, inverter inefficiencies, and transmission constraints are carefully modelled. Energy estimates also include the long-term degradation of modules and the balance of system components.
IEC Standards for Solar PV Plants
IEC requirements for the development of solar power plants are important to safety, quality, and project bankability. These standards define testing, certification, and performance requirements for PV modules, inverters, protection devices, and electrical components.
IEC compliance makes products consistent, conforms to grid codes, and gives lenders confidence. Certified photovoltaic power stations are less regulated and are more reliable over their lifecycle.
Photovoltaic Power Plant Cost Factors
The photovoltaic power plant cost depends on many interrelated factors. Land acquisition, site development and civil works are part of the initial investment. PV modules and inverters are the most expensive equipment components, while electrical balances of cables, transformers and switchgear can be especially valuable.
The costs of engineering services, power system studies, grid interconnection infrastructure, and evacuation lines are further impacted. In addition to CAPEX, lifecycle economics is directly related to operations and maintenance, performance monitoring, spare parts and equipment replacement.
Future Trends in Large-Scale Solar PV Plants
The large-scale photovoltaic power plants are incorporating more capacity and greater voltage levels to improve efficiency and reduce losses. Grid stability is being enhanced by new inverter technologies that include grid-forming and voltage support.
Peak shifting and frequency control are increasingly dependent on energy storage integration. And a variety of floating and hybrid installations are still being developed; digital monitoring, artificial intelligence and predictive maintenance are changing the long-term management of solar PV plant performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between a solar PV plant and a solar power plant?
One solar PV plant is a specific type of solar battery that produces electricity, while another term, which would be a solar power plant, may also mean solar thermal plants.
2. How does a utility-scale solar PV plant connect to the grid?
Utility-scale plants are connected through step-up transformers, switchyards and high-voltage transmission lines once their grid code has been met.
3. What factors affect the cost of a photovoltaic power plant?
All of the factors that impact total project cost include land, equipment quality, electrical infrastructure, engineering studies, grid evacuation, and long-term O&M costs.
4. Are floating solar PV plants more efficient than ground-mounted plants?
Cooling can boost the efficiency of floating plants, but it requires a higher degree of engineering and maintenance.5. Why are IEC standards important for solar PV plants?
IEC standards ensure the safety, reliability, regulatory approval, and financial bankability of solar photovoltaic power stations.